2020 |
||
| 9. | 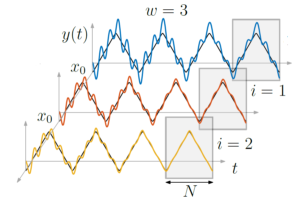 | R. Rozario; A. J. Fleming; T. Oomen Finite-Time Learning Control Using Frequency Response Data with Application to a Nanopositioning Stage Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 2085-2096, 2020, ISSN: 10834435. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanopositioning, Tracking Control @article{J20a,Learning control enables significant performance improvement for systems that perform repeating tasks. Achieving high tracking performance by utilizing past error data typically requires noncausal learning that is based on a parametric model of the process. Such model-based approaches impose significant requirements on modeling and filter design. This paper aims to reduce these requirements by developing a learning control framework that enables performance improvement through noncausal learning without relying on a parametric model. This is achieved by explicitly using the discrete Fourier transform to enable learning by using a nonparametric frequency response function model of the process. The effectiveness of the developed method is illustrated by application to a nanopositioning stage |
2019 |
||
| 8. | 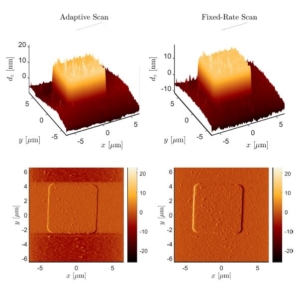 | K. Wang; M. G. Ruppert; C. Manzie; D. Nesic; Y. K. Yong Scan Rate Adaptation for AFM Imaging Based on Performance Metric Optimisation Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, (early access). Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: AFM, Nanopositioning, Scan Pattern, SPM, Tracking Control @article{Wang2019b,Constant-force contact-mode atomic force microscopy (AFM) relies on a feedback control system to regulate the tip-sample interaction during imaging. Due to limitations in actuators and control, the bandwidth of the regulation system is typically small. Therefore, the scan rate is usually limited in order to guarantee a desirable image quality for a constant-rate scan. By adapting the scan rate online, further performance improvement is possible, and the conditions to this improvement has been explored qualitatively in a previous study for a wide class of possible scan patterns. In this paper, a quantitative assessment of the previously proposed adaptive scan scheme is investigated through experiments that explore the impact of various degrees of freedom in the algorithm. Further modifications to the existing scheme are proposed and shown to improve the closed-loop performance. The flexibility of the proposed approach is further demonstrated by applying the algorithm to tapping-mode AFM. |
| 7. | 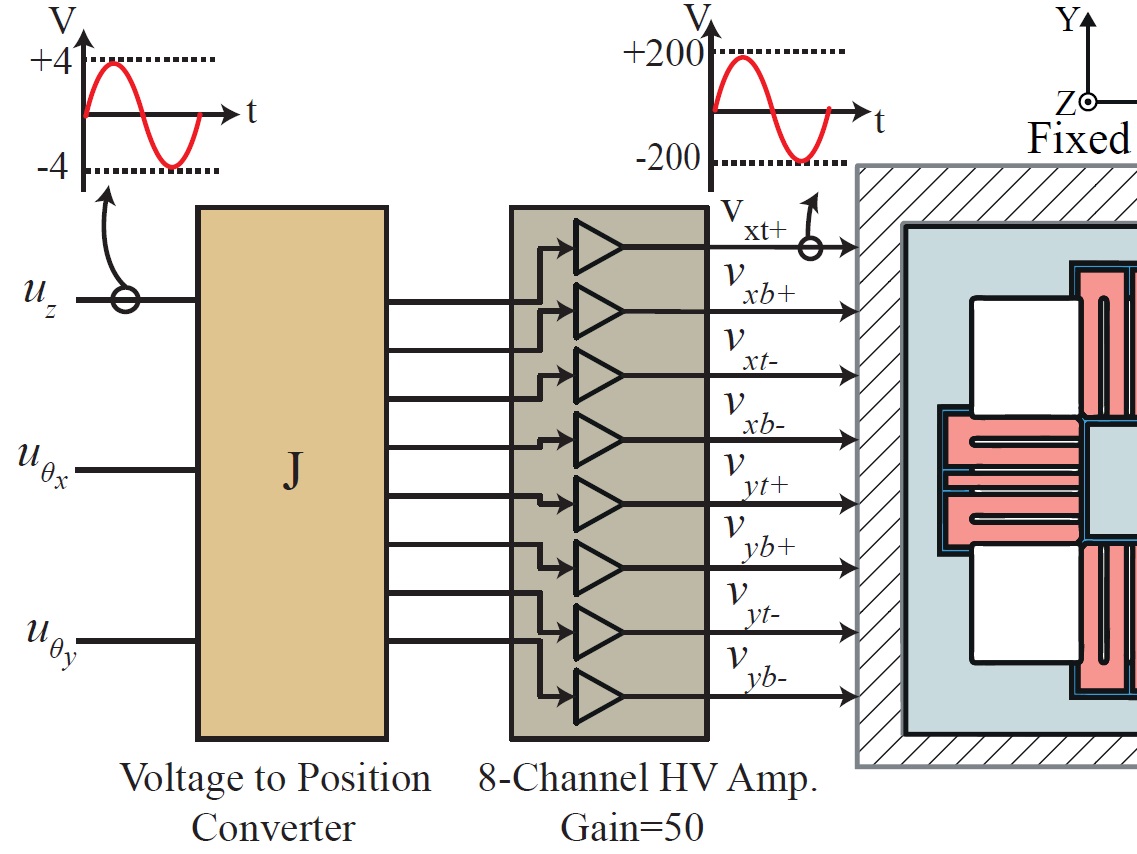 | M. Omidbeike; A. A. Eielsen; Y. K. Yong; A. J. Fleming Multivariable Model-less Feedforward Control of a Monolithic Nanopositioning Stage With FIR Filter Inversion Proceedings Article In: International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales (MARSS), Helsinki, Finland, 2019, ISSN: 978-1-7281-0948-0. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanopositioning, Tracking Control, Vibration Control @inproceedings{C19d,A model-less approach for inversion of the dynamics of multivariable systems using FIR filters is described. Inversion-based feedforward techniques have been widely used in the literature to achieve high-performance output tracking. The foremost difficulties associated with plant inversions are model uncertainties and non-minimum phase zeros. Various model-based methods have been proposed to exclude nonminimum phase zeros when inverting both single-input and single-output (SISO), and multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) systems. However, these methods increase the model uncertainty as they are no longer exact. To overcome these difficulties a model-less approach using FIR filters is presented. The results when applying the feedforward FIR filter to a multivariable nanopositioning system is presented, and they demonstrate the effectiveness of the feedforward technique in reducing the cross-coupling and achieving significantly improved output tracking. |
| 6. | 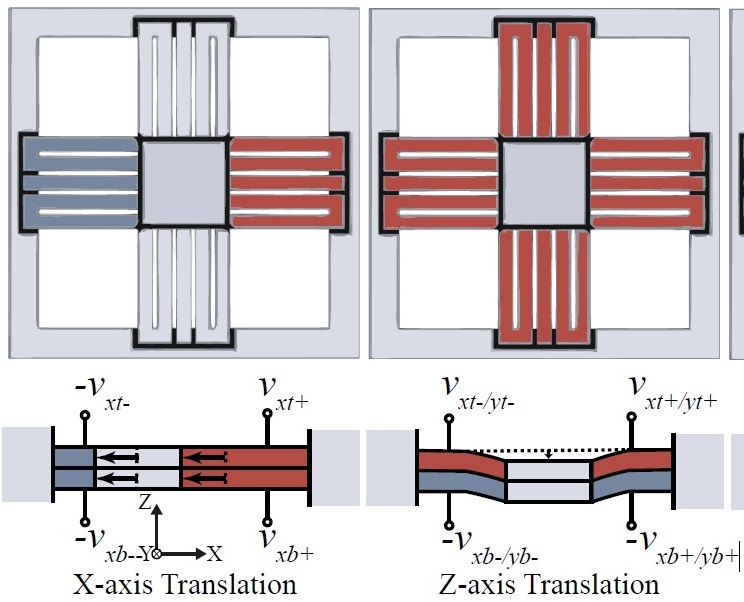 | M. Omidbeike; Y. K. Yong; S. I. Moore; A. J. Fleming A Five-Axis Monolithic Nanopositioning Stage Constructed from a Bimorph Piezoelectric Sheet Proceedings Article In: International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales , Helsinki, Finland, 2019, ISSN: 978-1-7281-0948-0. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanopositioning, Smart Structures, Tracking Control @inproceedings{omidbeike2019axis},The paper describes design, modeling and control of a five-axis monolithic nanopositioning stage constructed from a bimorph piezoelectric sheet. In this design, actuators are created by removing parts of the sheet using ultrasonic machining. The constructed nanopositioner is ultra-compact with a thickness of 1 mm. It has a X and Y travel range of 15.5 µm and 13.2 µm respectively; a Z travel range of 26 µm; and a rotational motion about the X-and Y-axis of 600 µrad and 884 µrad respectively. The first resonance frequency occurs at 883 Hz in the Z-axis, and the second and third resonance frequency appears at 1850 Hz, rotating about the X-and Y-axis. A decentralized control strategy is implemented to track Z, θx and θy motions. The controller provides good tracking and significantly reduces cross-coupling motions among the three degrees-of-freedom. |
| 5. | 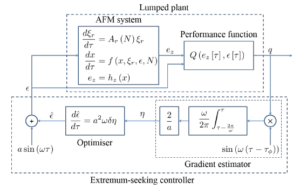 | K. Wang; M. G. Ruppert; C. Manzie; D. Nesic; Y. K. Yong Adaptive Scan for Atomic Force Microscopy Based on Online Optimisation: Theory and Experiment Journal Article In: IEEE Transactions on Control System Technology, 2019, (accepted for publication). Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: AFM, Nanopositioning, SPM, System Identification, Tracking Control @article{Wang2019,A major challenge in Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) is to reduce the scan duration while retaining the image quality. Conventionally, the scan rate is restricted to a sufficiently small value in order to ensure a desirable image quality as well as a safe tip-sample contact force. This usually results in a conservative scan rate for samples that have a large variation in aspect ratio and/or for scan patterns that have a varying linear velocity. In this paper, an adaptive scan scheme is proposed to alleviate this problem. A scan line-based performance metric balancing both imaging speed and accuracy is proposed, and the scan rate is adapted such that the metric is optimised online in the presence of aspect ratio and/or linear velocity variations. The online optimisation is achieved using an extremum-seeking (ES) approach, and a semi-global practical asymptotic stability (SGPAS) result is shown for the overall system. Finally, the proposed scheme is demonstrated via both simulation and experiment. |
2018 |
||
| 4. |  | A. Bazaei; Z. Cheng; Y. K. Yong; S. O. R. Moheimani A Novel State Transformation Approach to Tracking of Piecewise Linear Trajectories Journal Article In: IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 128 - 138, 2018. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanopositioning, Tracking Control @article{Bazaei2018,In this paper, we propose a novel approach for tracking of piecewise linear trajectories, such as triangular and staircase waveforms. We derive state and input transformations, which result in closed-loop error dynamics driven by a series of impulses. The proposed control structure takes the form of an output-feedback-feedforward system that is straightforward to implement. In contrast to the recently proposed tracking control methods for such trajectories, the closed-loop stability is not affected by the frequency of the desired triangular reference. The method is implemented on a nanopositioner serving as the scanning stage of an atomic force microscope. |
2017 |
||
| 3. | 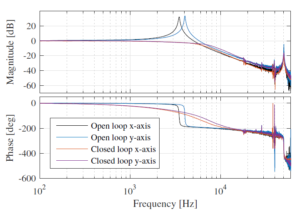 | M. G. Ruppert; M. Maroufi; A. Bazaei; S. O. R. Moheimani Kalman Filter Enabled High-Speed Control of a MEMS Nanopositioner Proceedings Article In: 20th IFAC World Congress, pp. 15554-15560, 2017. Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: MEMS, Nanopositioning, Tracking Control, Vibration Control @inproceedings{Ruppert2017b,We demonstrate a novel tracking controller formulation based on a linear time-varying Kalman Filter to regulate amplitude and phase of a reference signal independently. The method is applicable to sinusoidal references such as spiral, cycloid and Lissajous trajectories which are commonly used for imaging in high-speed Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). A Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) based nanopositioner, whose fundamental resonance frequency is dampened with an additional damping feedback loop, is employed. For a scan range of 2um, we demonstrate experimental tracking of sinusoids with frequencies as high as 5kHz, well beyond the open-loop fundamental resonance, with a tracking error of only 4.6nm. |
| 2. | 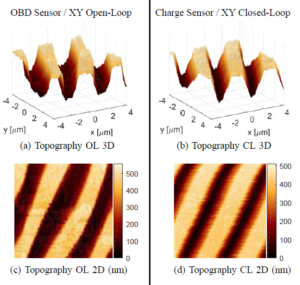 | M. Maroufi; M. G. Ruppert; A. G. Fowler; S. O. R. Moheimani Design and Control of a Single-chip SOI-MEMS Atomic Force Microscope Proceedings Article In: American Control Conference, 2017. Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: MEMS, Nanopositioning, SPM, Tracking Control @inproceedings{Maroufi2017,This paper presents a novel microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) implementation of an on-chip atomic force microscope (AFM), fabricated using a silicon-on-insulator process. The device features an XY scanner with electrostatic actuators and electrothermal sensors, as well as an integrated silicon microcantilever. A single AlN piezoelectric electrode is used for simultaneous actuation and deflection sensing of the cantilever via a charge sensing technique. With the device being operated in closed loop, the probe scanner is successfully used to obtain 8mmx8mm tapping-mode AFM images of a calibration grating. |
| 1. |  | M. G. Ruppert; A. G. Fowler; M. Maroufi; S. O. R. Moheimani On-chip Dynamic Mode Atomic Force Microscopy: A silicon-on-insulator MEMS approach Journal Article In: IEEE Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 215-225, 2017. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: MEMS, Nanopositioning, Piezoelectric Transducers and Drives, Sensors, Smart Structures, SPM, Tracking Control @article{Ruppert2017,The atomic force microscope (AFM) is an invaluable scientific tool; however, its conventional implementation as a relatively costly macroscale system is a barrier to its more widespread use. A microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) approach to AFM design has the potential to significantly reduce the cost and complexity of the AFM, expanding its utility beyond current applications. This paper presents an on-chip AFM based on a silicon-on-insulator MEMS fabrication process. The device features integrated xy electrostatic actuators and electrothermal sensors as well as an AlN piezoelectric layer for out-of-plane actuation and integrated deflection sensing of a microcantilever. The three-degree-of-freedom design allows the probe scanner to obtain topographic tapping-mode AFM images with an imaging range of up to 8μm x 8μm in closed loop. |
2020 |
||
| 9. |  | Finite-Time Learning Control Using Frequency Response Data with Application to a Nanopositioning Stage Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 2085-2096, 2020, ISSN: 10834435. |
2019 |
||
| 8. |  | Scan Rate Adaptation for AFM Imaging Based on Performance Metric Optimisation Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, (early access). |
| 7. |  | Multivariable Model-less Feedforward Control of a Monolithic Nanopositioning Stage With FIR Filter Inversion Proceedings Article In: International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales (MARSS), Helsinki, Finland, 2019, ISSN: 978-1-7281-0948-0. |
| 6. |  | A Five-Axis Monolithic Nanopositioning Stage Constructed from a Bimorph Piezoelectric Sheet Proceedings Article In: International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales , Helsinki, Finland, 2019, ISSN: 978-1-7281-0948-0. |
| 5. |  | Adaptive Scan for Atomic Force Microscopy Based on Online Optimisation: Theory and Experiment Journal Article In: IEEE Transactions on Control System Technology, 2019, (accepted for publication). |
2018 |
||
| 4. |  | A Novel State Transformation Approach to Tracking of Piecewise Linear Trajectories Journal Article In: IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 128 - 138, 2018. |
2017 |
||
| 3. |  | Kalman Filter Enabled High-Speed Control of a MEMS Nanopositioner Proceedings Article In: 20th IFAC World Congress, pp. 15554-15560, 2017. |
| 2. |  | Design and Control of a Single-chip SOI-MEMS Atomic Force Microscope Proceedings Article In: American Control Conference, 2017. |
| 1. |  | On-chip Dynamic Mode Atomic Force Microscopy: A silicon-on-insulator MEMS approach Journal Article In: IEEE Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 215-225, 2017. |
