2018 |
||
| 5. | 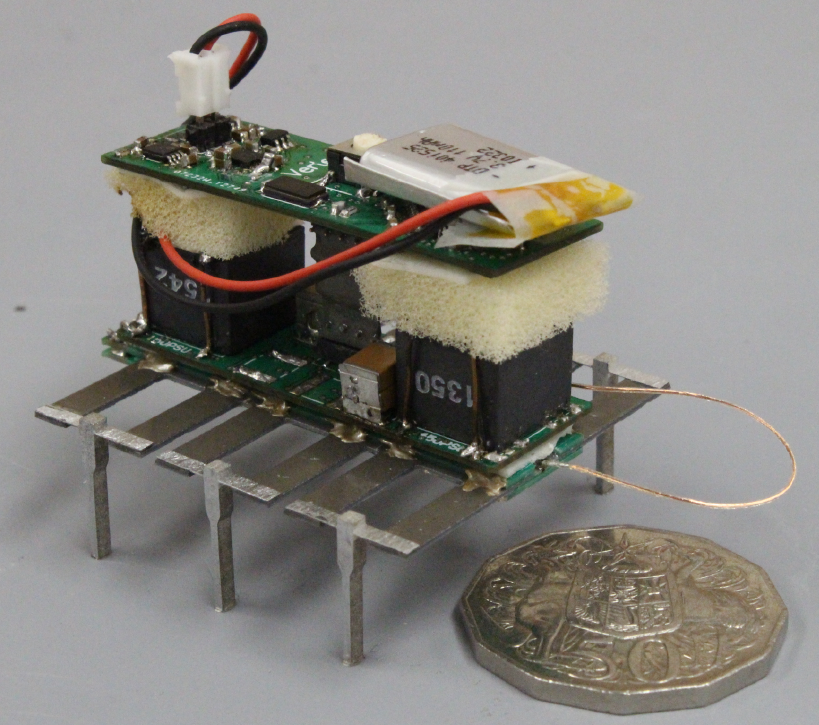 | S. A. Rios; A. J. Fleming; Y. K. Yong Monolithic Piezoelectric Insect with Resonance Walking Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 524-530, 2018, ISSN: 10834435. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Robotics @article{J18a,This article describes the design, manufacture and performance of an untethered hexapod robot titled MinRAR V2. This robot utilizes a monolithic piezoelectric element, machined to allow for individual activation of bending actuators. The legs were designed so that the first two resonance modes overlap and therefore produce a walking motion at resonance. The monolithic construction significantly improves the matching of resonance modes between legs when compared to previous designs. Miniature control and high voltage driving electronics were designed to drive 24 separate piezoelectric elements powered from a single 3.7 V lithium polymer battery. The robot was driven both tethered and untethered and was able to achieve a maximum forward velocity of 98 mm/s when driven at 190 Hz and 6 mm/s at 5 Hz untethered. The robot is capable of a wide range of movements including banking, on the spot turning and reverse motion. |
2017 |
||
| 4. | 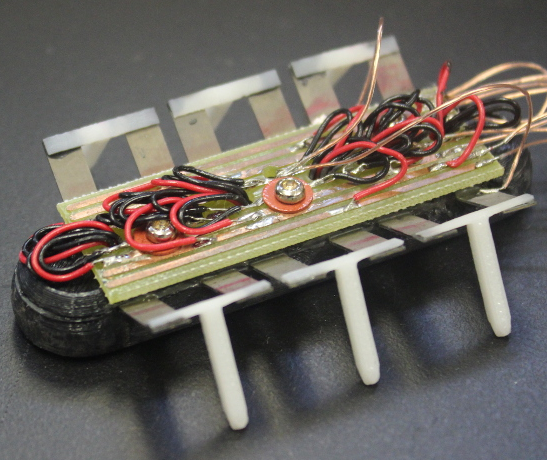 | S. A. Rios; A. J. Fleming; Y. K. Yong Miniature Resonant Ambulatory Robot Journal Article In: IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 337–343, 2017, ISSN: 2377-3766. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Robotics @article{J17a,This article describes the design, manufacture, and performance of a prototype miniature resonant ambulatory robot that uses piezoelectric actuators to achieve locomotion. Each leg is comprised of two piezoelectric bimorph benders, joined at the tip by a flexure and end effector. Combinations of amplitude and phase can be used to produce a wide range of motions including swinging and lifting. A lumped mass model previously developed is described as a design tool to tune the resonance modes of the end effector. The completed robot was driven with frequencies up to 500 Hz resulting in a maximum forward velocity of approximately 520 mm/s at 350 Hz. A frequency analysis was also performed to determine the effects of ground contact on the performance of the robot. This analysis showed a significant reduction in the resonance gain and frequency. |
2016 |
||
| 3. | 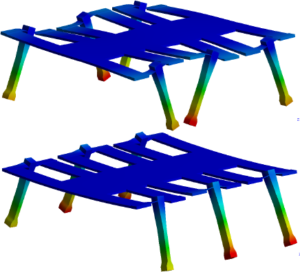 | S. A. Rios; A. J. Fleming; Y. K. Yong Design and Characterization of a Minature Monolithic Piezoelectric Hexapod Robot Proceedings Article In: IEEE Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Banff, Canada, 2016. Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Robotics @inproceedings{C16h,This paper describes the design, construction and resonant performance of a monolithic piezoelectric miniature hexapod robot. The miniature robot operates by driving the piezoelectric elements at the mid point between the first and second resonance modes to produce an ambulatory motion. The monolithic robot was milled out of a single piece of outwardly poled piezoelectric bimorph using an ultrasonic milling machine. Silver electrodes were evaporated onto the bimorph to isolate the individual piezoelectric elements from each other. The leg end-effectors of the robot were milled out of aluminium and a previously described lumped mass model was used to design the end-effector for the leg such that the swinging and lifting resonant modes were closely matched. The finished robot attained a swinging and lifting resonance frequency of 300 Hz and 330 Hz with a 5 Hz and 7 Hz spread between legs respectively. |
| 2. | 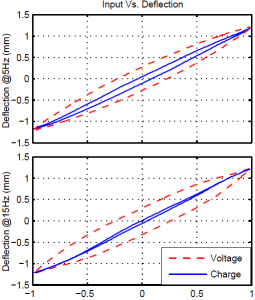 | S. A. Rios; A. J. Fleming Design of a Charge Drive for Reducing Hysteresis in a Piezoelectric Bimorph Actuator Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 51-54, 2016. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Piezoelectric Transducers and Drives, Robotics @article{J16f,This article describes the design of a charge drive for reducing the hysteresis exhibited by a piezoelectric bimorph bender. Existing charge drive circuits cannot be directly applied to bimorph benders since they share a common electrode. In this article a new charge drive circuit and electrical configuration is implemented that allows commonly available piezoelectric bimorphs to be linearized. This circuit consists of four major components, including, a high voltage amplifier, a differential amplifier, a piezoelectric load and a PI feedback controller. An isolation amplifier was used to achieve a differential amplifier with a high common-mode rejection ratio. The charge drive was tested by driving a series poled, three layer bimorph bender. The results demonstrate that the use of a charge drive can reduce the hysteresis from 26.8% to 2.1%. This work has identified an alternative feedforward method to improve the AC hysteresis performance of a piezoelectric bender by using a charge drive. |
2015 |
||
| 1. |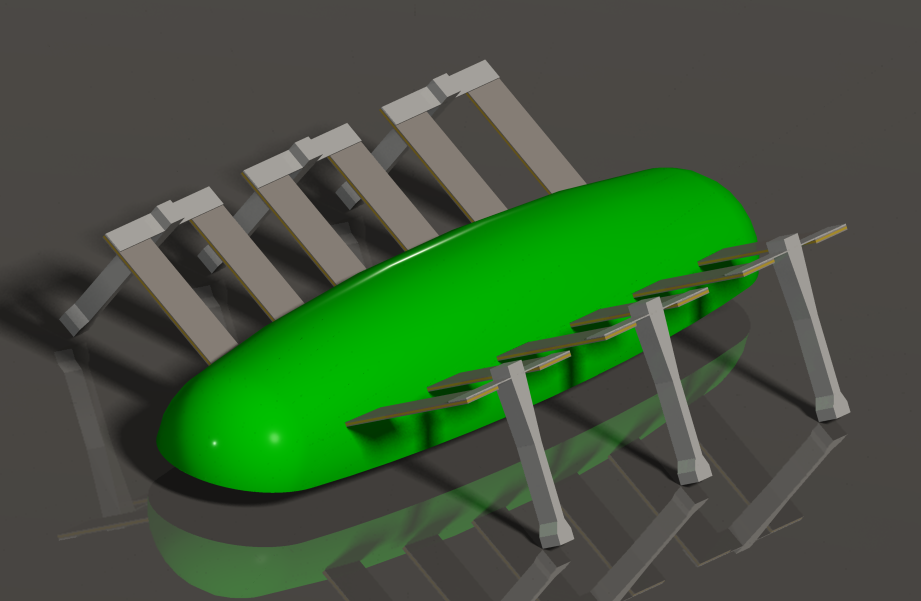  | S. A. Rios; A. J. Fleming; Y. K. Yong Design of a two degree of freedom resonant miniature robotic leg (Invited Paper) Proceedings Article In: IEEE Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Busan, Korea, 2015. Links | BibTeX | Tags: Robotics @inproceedings{C15b, |
2018 |
||
| 5. |  | Monolithic Piezoelectric Insect with Resonance Walking Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 524-530, 2018, ISSN: 10834435. |
2017 |
||
| 4. |  | Miniature Resonant Ambulatory Robot Journal Article In: IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 337–343, 2017, ISSN: 2377-3766. |
2016 |
||
| 3. |  | Design and Characterization of a Minature Monolithic Piezoelectric Hexapod Robot Proceedings Article In: IEEE Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Banff, Canada, 2016. |
| 2. |  | Design of a Charge Drive for Reducing Hysteresis in a Piezoelectric Bimorph Actuator Journal Article In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 51-54, 2016. |
2015 |
||
| 1. |  | Design of a two degree of freedom resonant miniature robotic leg (Invited Paper) Proceedings Article In: IEEE Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Busan, Korea, 2015. |
